During the COVID-19 crisis, many companies introduced new communication solutions on very short notice, with little consideration given to data security and data privacy. Seven steps that those in charge of IT can use to increase the level of protection.
When companies introduce new tools, they are at first primarily concerned with the budget for installation, licensing requirements and potential operations - and of course the approval processes. Compliance and data privacy are often not considered until a later stage.
But in fact, companies should consider these issues right from the beginning, as 320 fines totaling more than EUR 490 million were issued with regard to the General Data Protection Regulation by August 2020, including EUR 26 million in Germany.
To avoid hefty fines, all processes involving personal data must be checked for GDPR conformity and documented. Therefore, all new tools and systems must be investigated with regard to IT security and data privacy. It is precisely these two aspects that are considered the biggest obstacle for digitization by 54.6 percent of those surveyed for the Future IT Report 2020. The COVID-19 crisis forced many companies to quickly introduce collaboration tools despite any concerns that they might have had. Their impact on data privacy and IT security must now be analyzed and improved. This should be done on the basis of the following seven points.
Steps to increase IT security
Usually, collaboration tools such as Microsoft Teams can be installed in just a few steps. Even the standard settings ensure productive work from home and offer a contemporary communication platform. But often, companies only did what was absolutely necessary to integrate Teams into the existing IT infrastructure because of time constraints. The questions below demonstrate why action is required:
- Which existing communication solutions are used simultaneously, and what is the best way to integrate them with Microsoft Teams?
- Which functional areas in Microsoft Teams can replace existing communication solutions, and what might such a process look like?
- How can IT security be guaranteed in a comprehensive and integrated fashion, both in the on-premises IT infrastructure as well as in the Microsoft Cloud?
- How can productivity be maintained and increased while also reducing complexity in order to keep support requirements low?
The protection of identities is particularly important in hybrid Cloud environments. The “Zero Trust” principle is used to provide protection regardless of the location. It consists of the application-spanning checking and risk assessment of identities at all times and in all processes. This approach ensures rapid and targeted responses to the relevant attack scenarios. The following technologies provide sustained protection of identities:
- Multi-factor authentication prevents the misuse of stolen identities
- Limited access, so log-ins involving compromised or risky identities are automatically prevented
- Password protection to identify and prevent weak or compromised passwords
- Non-password log-ins, e.g. FIDO2 security key
- Assignment of privileged authorizations, possibly limited to the required time period (where applicable)
The loss of digital information can become an existential threat. The GDPR also requires adequate protection for relevant digital information. The (un)intentional sharing, modification and deletion of information as well as the theft and undesirable loss of data must be identified and prevented.
The classification and labeling of information with confidentiality levels ensure targeted automated measures for preventing the loss of confidential data. Using encryption, it can be protected from non-authorized access across devices and applications during the entire life cycle. Storage identifiers ensure the availability of data, even if it has been (un)intentionally damaged or deleted. They also contribute to data frugality by automatically deleting data after the defined retention periods have expired.
Steps to increase data protection
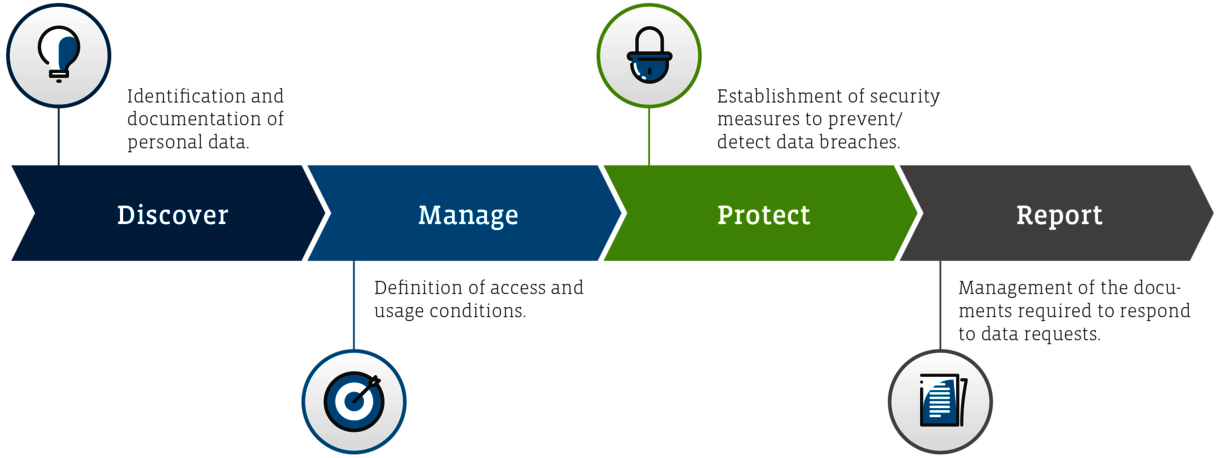
Personal data can be found in many places at the company. When it comes to collaboration tools, at minimum the employee data must be taken into account. This includes company e-mail addresses as well as the first and last name of each employee. From a data privacy point of view, a subsequent data privacy assessment (DSFA) including risk assessment must be performed before someone is allowed to work with a collaboration tool. This assessment must be completed immediately if it was initially omitted on account of the crisis situation. A risk assessment must be performed even if a DSFA is not required.
After the personal data has been identified and documented, the new processing workflows are added to the existing data privacy documentation (list of processing activities). In this context, it is important to verify whether the company already has established directives for using the new tool, e.g. for Remote Work or Bring your own Device. Otherwise, companies have to develop and implement such directives. Regarding the principle of data frugality, roles and responsibility with regard to accessing, managing, storing and deleting data within the new tool must also be clarified.
The GDPR requires companies to implement the appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data. In the case of a breach, the competent authorities must be informed within 72 hours, and specific persons must also be notified in some cases. Therefore, such documented and verifiable technical-organizational measures must be implemented for each new tool.
Companies must also be able to provide evidence of how they collect, use, store, transfer and destroy personal data. For example, Microsoft provides Teams customers with the appropriate services that assist with the administration of the required documents. They include Security and Compliance Centers or Audit Logs.